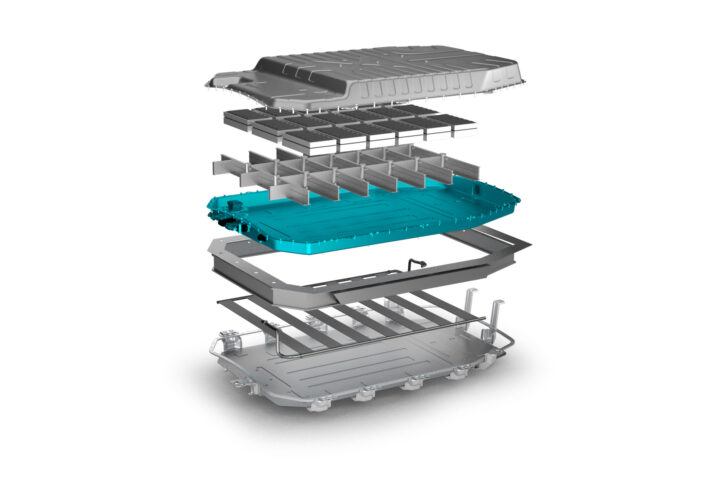
Thermal management of BEVs: Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Die Inhalte dieser Seite sind leider nicht auf Deutsch verfügbar.
mit Google übersetzenArticle | 21. Juli 2022
As we continue to move towards new mobility and the electrification of vehicles in general, the thermal management of batteries has come to the forefront as a critical element that must be addressed. Thermal management in Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) is related to temperature regulation of the battery in order to keep its optimal working conditions at all times. The performance of a battery is inextricably linked to its temperature, which has an impact on areas such as the time it takes to charge, its ability to sustain capacity, and its health and performance overall. At the same time, temperature regulation is very important for the safety of passengers as overheating and potential thermal runaways can put passengers at risk.
Thermal management requires
special materials
Material developers at Datwyler, a provider of system critical, high-performance polymer products, have been working to develop thermally conductive materials to support the thermal management of BEVs, including thermal interface materials (TIMs).
TIMs, by conducting the heat away from the source to the cooling systems, help to keep the optimal temperature of battery systems. The cooling or heating ability of these materials is directly linked to the thermal conductivity described as lambda and is expressed in W.mK.
There are various forms and types of TIMs, whether it is conventional “solid” rubber compounds, foams, resins, adhesives and others. Apart from others, these materials can be processed as form-in-place (foams, adhesives, resins, and generally thermo-setting materials) and in the form of stand-alone gaskets (rubber compounds).
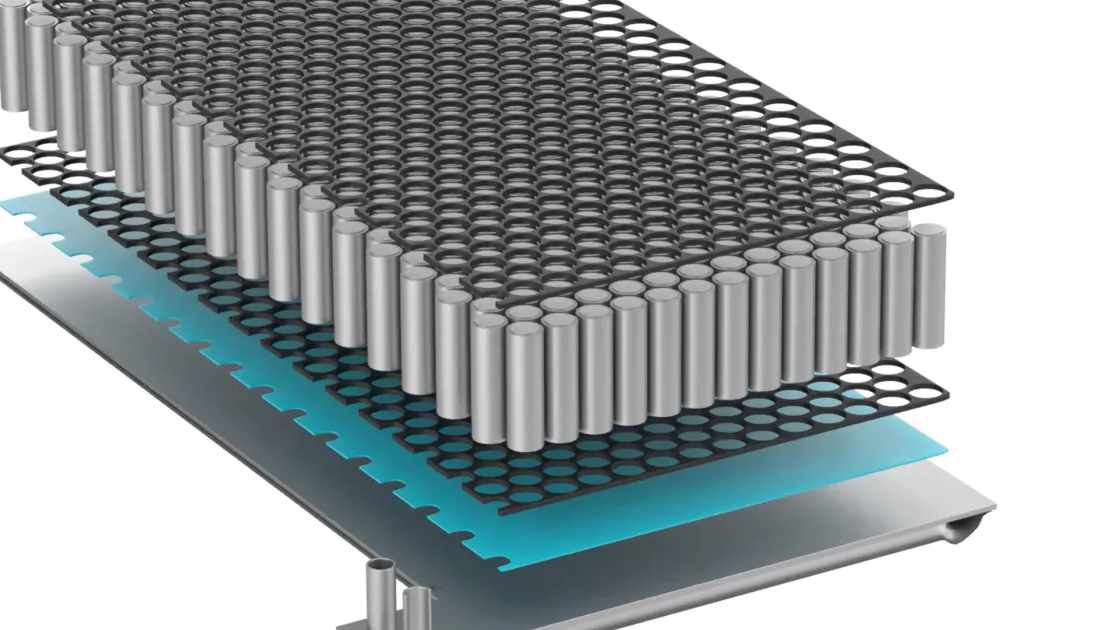
What are thermal interface materials?
At Datwyler we have been focusing on stand-alone gasket solutions based on various polymer matrices. Stand-alone gaskets have certain benefits in comparison to form-in-place solutions. First and foremost, it allows for recyclability of battery packs where the system can be completely disassembled at the end of its lifetime.
Form-in-place solutions often “glue” different parts of the battery pack inseparably together. The composition of a rubber compound for a stand-alone gasket can also be adjusted according to specific environments, it is lightweight and flexible and it allows integration of additional material properties such as electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.

Thermal Interface Materials
Material development expertise delivers many benefits
A benchmarking study of our materials, which draws direct comparisons to other sealing solutions providers, in addition to advanced simulations, shows that the performance of our material under selected fast-charge conditions shows a decrease in the cell temperature of approximately 6K when compared to the industrial standard – which is considered to be at a level around 1 W.mK. Such a decrease in temperature gives passengers an additional element of safety and can indirectly create “space” for even faster charging supporting the latest generation of superchargers. This can also help to prevent overheating of batteries and creation of dendrites, ensuring optimal long-term performance at high-efficiency levels.
In addition to leading the way in terms of thermal conductivity of conventional sealing rubber compounds, Datwyler is also able to optimize these compounds in-house, taking into consideration the surrounding environment, the density of these materials and their hardness. Weight is also taken firmly into consideration, as lightweighting is vital to extending the range of BEVs. Literally, every gram matters and it is therefore imperative not only to focus on thermal conductivity, but also on material performance and the balance of all properties.
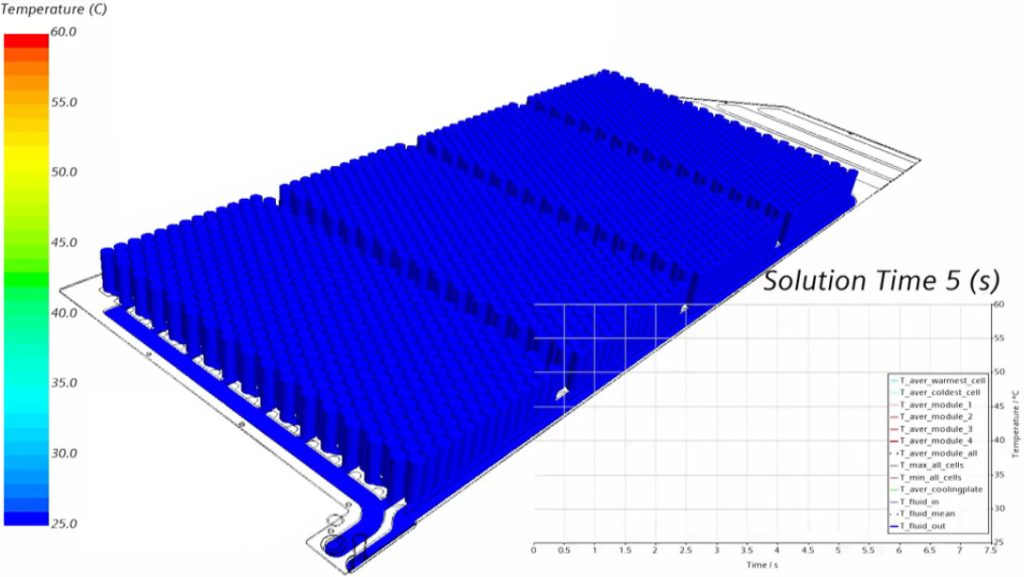
Thermally conductive compounds developed by Datwyler show material density below 2 g.cm3, and can be as low as half of our closest competitor. This translates to a saving of 1.8 kg weight in the design selected for the advanced simulation study.
Continuous improvement is driven via dedicated projects
To help our customers in the transition to e-mobility, Datwyler is expanding its in-house capabilities not only through a focus on thermally conductive materials but also in the aforementioned electrically conductive and EMI shielding materials, all of which are covered within Project ETEMI™.
Project ETEMI™ covers material development ranging from conventional elastomers to liquid silicon rubber (LSR) and thermoplastics. The aim is to ensure that customers diversifying towards hybrid and battery electric vehicles are able to realize the full potential of system critical sealing components with enhanced functionality – such as sealing the battery pack with thermally conductive elastomer materials to provide protection from the environment and support in terms of heat transfer from the battery.
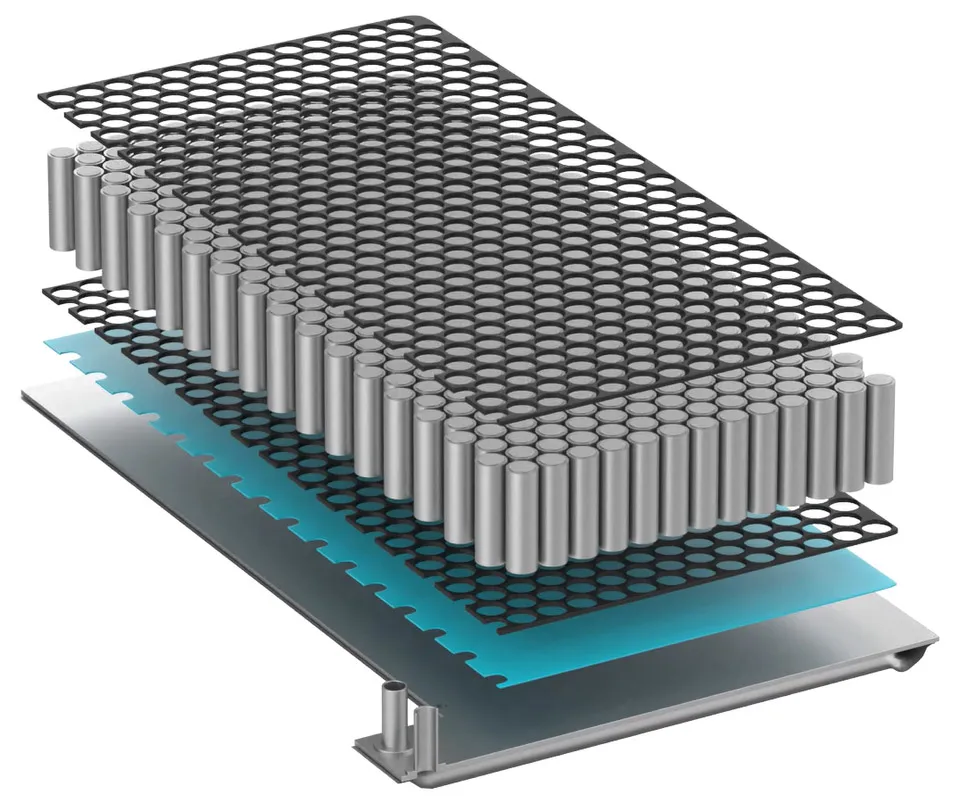
Ultimately, ETEMI™ will be the catalyst for the creation of a material matrix whereby electrical and thermal conductivity and EMI shielding can be coupled and decoupled to suit a wide variety of applications.
Read more about the project ETEMI™:
Author
For more information or to speak to a Datwyler expert, please contact us.
Dr. Hediyeh Zahabi
Manager Material Development
Innovation & Design